Communication is key to the development of human society. Back in the days when tribes lived on their own, spread out all over the place, the growth of the community was limited to the resources they had in their vicinity. The resources referred to aren't only restricted to natural ones, but also the diversity of the gene pool. If everyone married each other without outsiders involved, inbreeding would occur at some point.
When travel was made available and tribes started to come in contact with each other, that's when the need for communication arose, and with it, a more thriving society for all involved.
This same scenario can be applied to the crypto space when talking about blockchains. Many of them are often referred to as siloed entities, each with its own ecosystem but not always easy for users of each system to talk to each other from different blockchains.
Cross-chain operability and communication are the logical next step forward for the development of this space. A few blockchain projects had already started R&D to tackle this problem, amongst them the Polygon network. Together with Polkadot and Cosmos, Polygon positions itself to be the one layer on the Ethereum network that connects other blockchains built into the Ethereum ecosystem so everyone can talk to each other in a seamless manner.
Polygon is a critical component of the Ethereum network, not just as a scaling solution and resolution to the high gas fees and low throughput on the Ethereum network, but as an interoperability layer as well. This Beginner's Guide to Matic will not only highlight the importance of Polygon and its robust utilities, but it will also answer the important question: What is Polygon?
Page Contents 👉
- 1 What is Polygon? Summary:
- 2 Key Features of Polygon are:
- 3 Polygon Pros and Cons
- 4 A Brief History of Polygon Network
- 5 What is Polygon Network?
- 6 What is the Polygon MATIC token used for?
- 7 What are Ethereum Scaling Solutions?
- 8 Why is Polygon good for Ethereum?
- 9 Polygon (MATIC) vs. Ethereum Layer 1
- 10 Polygon (MATIC) Price and Potential
- 11 How to Buy MATIC Cryptocurrency
- 12 Where to store MATIC Tokens
- 13 Top Projects on Polygon
- 14 Polygon (MATIC) Review: Closing Thoughts
What is Polygon? Summary:
Polygon is an interoperability and scaling framework for building Ethereum-compatible blockchains. Polygon helps to significantly increase the efficiency of the Ethereum network both in terms of lowering fees and increasing transaction throughput by acting as what is known as a “sidechain“.
The Polygon network is a blockchain running next to the main Ethereum blockchain network, it alleviates the burden of processing transactions from the Ethereum network by doing this on its own chain at a much faster speed, allowing for lower gas fees as a result. It also serves to connect other Ethereum-based blockchain applications together while also providing a toolset to simplify the building process for the apps, earning it the nickname “Ethereum's Internet of Blockchains”.
It aims to combine the networks' adaptability and scalability while taking advantage of Ethereum's security, liquidity, and interoperability. The Polygon network is centred around the MATIC token, which is used for governance, staking, and fees. The Polygon blockchain aims to be the blockchain of choice for anyone looking to build an Ethereum-compatible blockchain project. It offers a framework to help builders get started with a variety of tools at their disposal and connectivity for the blockchain to talk to the Ethereum network and other blockchains in the same space.
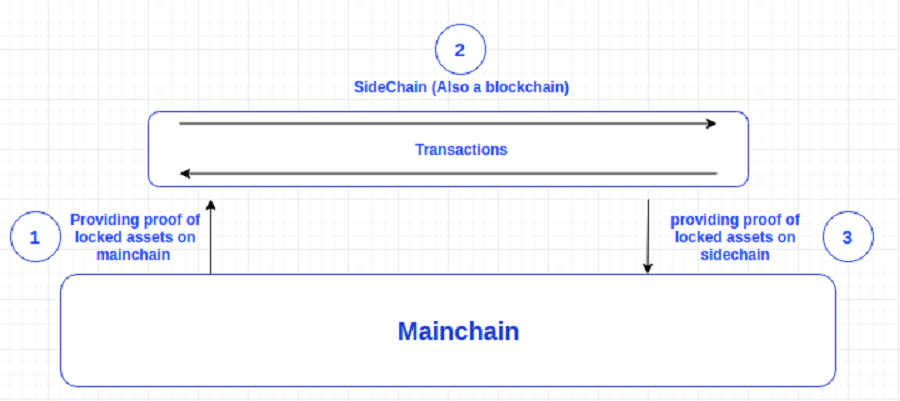
Illustration of a side chain in cryptocurrency. Image via StackExchange
Key Features of Polygon are:
-
Quick and safe transactions: The Polygon network can perform an estimated 65,000 transactions per second, far more than what Ethereum can manage. A single sidechain alone can process up to 10,000 transactions. At the same time, it leverages the security of the Ethereum blockchain by having the final confirmation processed there.
- ETH-compatibility: Polygon offers builders full Ethereum compatibility with their blockchain projects. They can easily launch them on Polygon and gain access to the Ethereum network with ease.
-
zk-EVM: Polygon is one of the earliest blockchains to use this technology. The “zk” stands for “zero-knowledge”, a way to prove you have something without having to show what you have. Previously, this method didn't work with smart contracts but by adding the EVM component to it, this method can also be used with smart contracts. This means much quicker and more secure transactions. It also allows developers to build a variety of dApps for all sorts of user experiences.
-
“Security as a service”: This feature gives builders the option to utilise Ethereum's validators to validate transactions or for professional validators to do so.
Polygon Pros and Cons
Pros of Polygon Matic
- Fast and cheap transactions- not only compared with Ethereum but it can stand its own in this corner with other blockchains of a similar kind.
- High level of security- by using the Ethereum network for its own security layer. Its own sidechain also uses Proof-of-Stake for additional security.
- High-profile partners– the Polygon marketing team had gone into overdrive by signing up with numerous high-profile partners such as Starbucks and Nike to name a few. It was also accepted into Disney's Accelerator Program, which bodes well for the future of mainstream adoption of the blockchain.
- Healthy ecosystem– lots of popular dApps are on the Polygon network which gives it a high user rate, driving demand for its native token.
Cons of Polygon Matic
- Not a standalone chain– It relies heavily on the Ethereum chain, tying its fortunes with Ethereum.
- Heavy competition– Polygon is not the only kid on the block bringing a scaling solution to Ethereum. It's also one of a handful of blockchain projects working on cross-chain communication, albeit within the Ethereum space but not yet with other non-Ethereum-based chains.
- Centralization concerns- Polygon is more centralized as it is managed and developed by centralized entities, which is in contrast to decentralized cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin.
A Brief History of Polygon Network
The Polygon network would not have come about if it weren't for the NFT project CryptoKitties. Back in 2017, that was the most talked-about project on the Ethereum blockchain and within the crypto community. Its popularity caused terrible network congestion on the blockchain and traders had to pay exorbitant fees. Jaynti Kanani, a data scientist in India who was working for Housing.com, noticed this issue and saw an opportunity for improvement. He reached out to Sandeep Nailwal, a blockchain developer, and Anurag Arjun, a business consultant for help. They got together and drafted a white paper, calling their project MATIC network. Their center of operations was set up in Mumbai.
Later in April 2019, the Polygon team sold about 1.9 billion MATIC tokens to raise funds for developing the project through the Binance launchpad in an IEO (Initial Exchange Offering). The main MATIC network successfully launched in Q2 of 2020.
In February 2021, the team rebranded itself as Polygon. The rebrand represents a shift in the team's focus from developing Plasma chains to an expansion of the project's services, including the use of multiple scaling solutions. During this transition, they were joined by Mihailo Bjelic, a Serbian who brought his expertise in software engineering, to the team.
Since then, the strength of the project has grown by leaps and bounds. Its mission is to be the top aggregator of Ethereum-compatible blockchains by providing them with superior interoperability capability while also processing transactions made on the Ethereum network to help speed up the process.
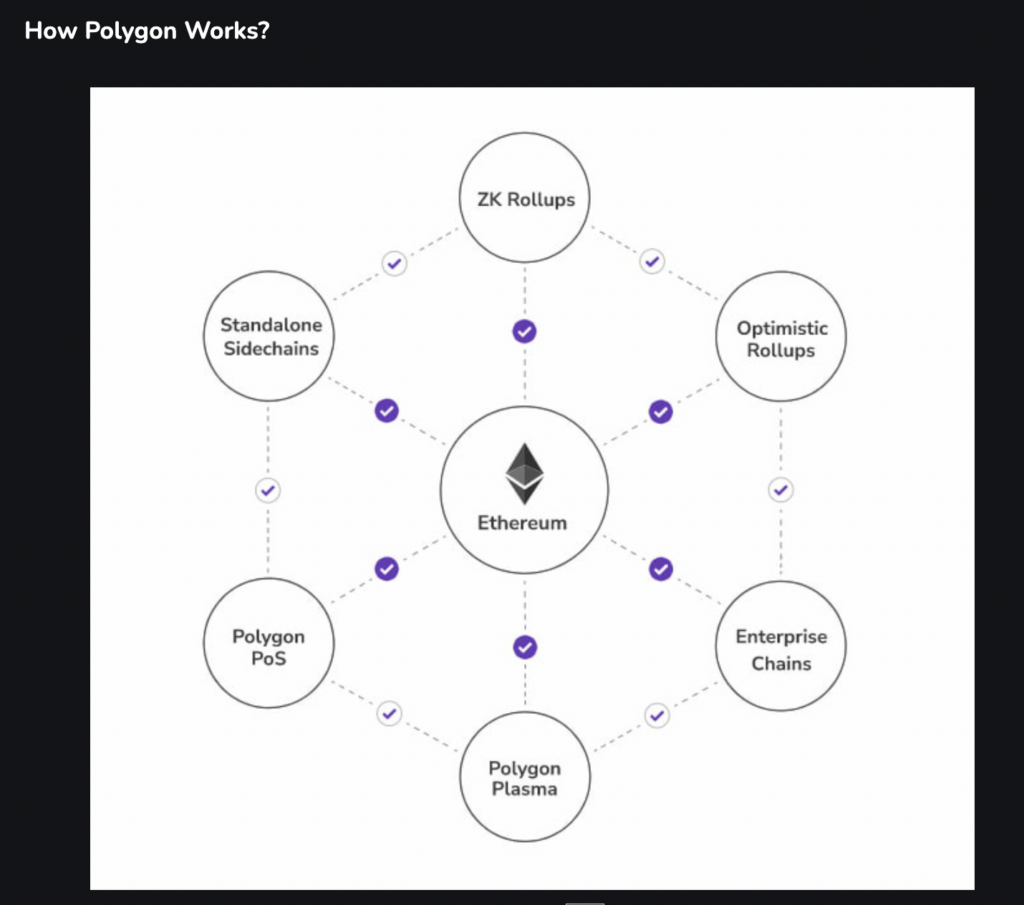
What is Polygon Network?
In the English language, “poly” is often used to talk about something that is multi-faceted. While a pentagon has 5 sides and a hexagon has 6, a polygon has an infinite number of sides. This is the idea behind the Polygon network, a blockchain project with multiple facets to serve the main Ethereum network.
There are two components to the Polygon network: a sidechain scaling solution for the Ethereum network known as Matic, and as an interoperability platform for Ethereum-based blockchains.
The Matic component is a sidechain that uses the Plasma scaling solution to help Ethereum process transactions much faster and at a cheaper price. It addresses the deficiencies found in the Ethereum network, which are low transaction speeds and high gas fees. You can think of it as a contractor tasked by Ethereum to do the heavy lifting of transaction processing.
After its rebranding, it broadened its offerings with the second component, which is by becoming the platform for launching interoperable blockchains on the Ethereum mainnet. Polygon provides the framework for connectivity by allowing messaging between the blockchains and the Ethereum network itself and also enabling interoperability for existing blockchains.
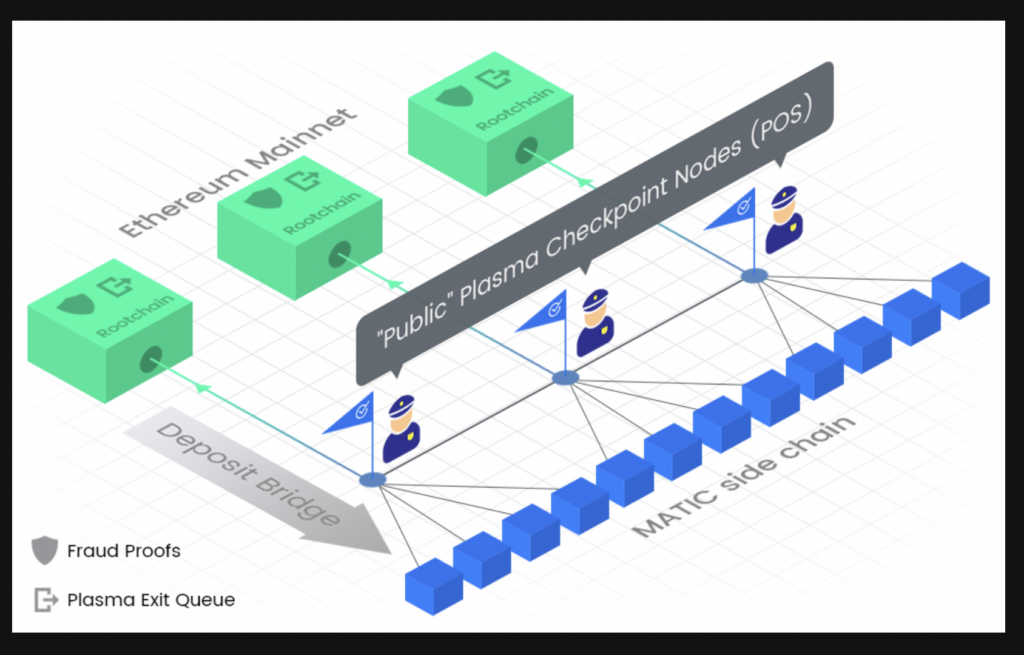
Polygon PoS Sidechain
The PoS sidechain runs alongside the Ethereum mainnet to process transactions before passing them to Ethereum for final confirmation. This part of the process is done through checkpoints and fraud proofs. The side chain can process up to 7000 transactions per second at a fraction of the Ethereum gas fee.
PoS sidechain uses its own Proof-of-Stake mechanism to run the blockchain. A 2/3 majority is required to reach a consensus on block validation. Validators are known as Stakers in this environment. Anyone can become a validator by staking any amount of MATIC tokens on the Ethereum chain and run a full node.
The side chain supports two types of bridges for moving assets between itself and Ethereum: Plasma Bridge and the PoS Bridge. The former is more secure but there is a 7-day withdrawal period due to the fraud-proof mechanism. The latter is secured by a set of validators, using the security layer mentioned below
Smart Contract Layer
This layer houses a collection of smart contracts with the following functions:
Delegation management – manage the delegators who delegate their tokens to validators for staking purposes.
Staking management – handle all staking-related functions
Record maintenance – checkpoint records and snapshots of the states of the side chain are stored here.
Heimdall Node
Here is where the validation of transactions takes place. A checkpoint is created after a number of blocks are validated to ensure continuity in the validation process. The layer itself is based on the Tendermint consensus with changes made to the signature scheme and different data structures. A Merkle Tree is created here by aggregating the blocks generated by the Bor layer. Periodically, it also publishes the Merkle tree root information to the Ethereum blockchain.
The checkpointing process is important because once past it, the transactions will be written on the Ethereum blockchain forever. This is known as finality. If there are any assets withdrawn as part of the transaction, the checkpoints will also provide “proof of burn”.
PoS validators run this type of node to validate transactions. Each validator is given any number of 10-token slots, based on the amount of MATIC tokens staked on the Ethereum blockchain.
Bor Node
This layer handles block production for the Polygon PoS Chain. Block producers are selected by the validators based on Tendermint’s proposer selection algorithm that chooses from the validators.
Delegators are MATIC token holders who have no interest in being a validator themselves but would like to help secure the network. They do so by delegating their tokens to the existing pool of validators. Care is to be exercised in selecting a validator so that their tokens are not slashed by malicious actors. If the staked tokens are to be withdrawn, there is a holding period of 9 days before the delegators can regain access to their tokens.

A visual diagram of the 3 layers in the PoS Sidechain. Image via Polygon Wiki
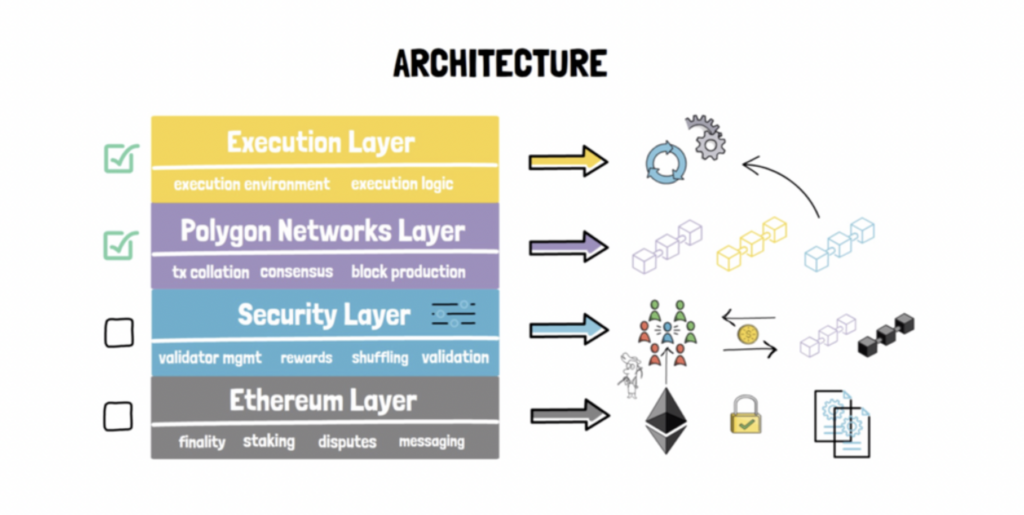
Architecture of the Polygon Network
Aside from the sidechain portion, the Polygon network features a 4-layer layout to help blockchains be connected to Ethereum to take advantage of the Ethereum ecosystem while keeping their own distinctiveness as an individual blockchain.
Ethereum Smart Contract Layer
Critical functions to be handled by Ethereum occur here in the form of smart contracts. These include functionality such as finality of the transactions, staking, dispute resolutions, and cross-chain messaging. This is an optional layer because many of these functions can be handled by the blockchains themselves or if they do not require finality of the transactions to be on the Ethereum blockchain.
Security Layer
Blockchains that want to make use of this layer can choose to pay professional validators for their validation services for a fee. If this layer is implemented directly, then they will be using Ethereum's validators to perform the validation. This layer runs in parallel to the Ethereum network. The two main functions handled here are validator management and Polygon Chains validation.
Polygon Networks Layer
Any blockchain built on Polygon resides here. They belong to one of two types: either as a standalone chain or a secured chain. These blockchains do their own block production, have their own consensus mechanism, and collate their own transactions. The biggest difference between them is that the secured chain opts into the security layer while the standalone chain doesn't.
Execution Layer
This layer validates and executes transactions originating from the Polygon Network layer. It has an execution environment and logic to handle the transactions. This is a mandatory layer that the blockchain networks need to use.
Polygon SDK
The Polygon SDK is a set of tools and modules that simplifies blockchain development that is EVM-compatible. Some of these include consensus algorithms, synchronization protocols, and various other modules that make it possible to build standalone chains or secure chains. The idea is to be a one-stop shop for developers to launch their projects on Ethereum with a single click.
What is the Polygon MATIC token used for?
MATIC is the native cryptocurrency used on the Polygon network. It is the method of payment used to pay for the cost of having your transaction data stored on the Polygon network. As the number of projects on Polygon increases, the demand for the token also goes up exponentially.
Aside from this, MATIC is also a governing token that gives holders the ability to vote on proposals aimed at furthering the development of the blockchain project. Examples of this are new scaling solutions that are considered for adoption by the community.
Holders of the MATIC token can stake them to help secure the Polygon standalone chain PoS and earn some yield at the same time. Staking MATIC through Ledger is one of the safest ways to do so as it combines the security of a hardware wallet with the flexibility to choose your own validator. You can find Matic and other staking tokens in our Top Staking Tokens article.
What are Ethereum Scaling Solutions?
When Ethereum was initially designed, the designers were faced with the blockchain trilemma of decentralisation, security, and scalability. In the end, they decided to put more emphasis on the first two with the idea of improving the last one at a later stage. At that time, it was difficult to accurately predict how popular the Ethereum blockchain would be.
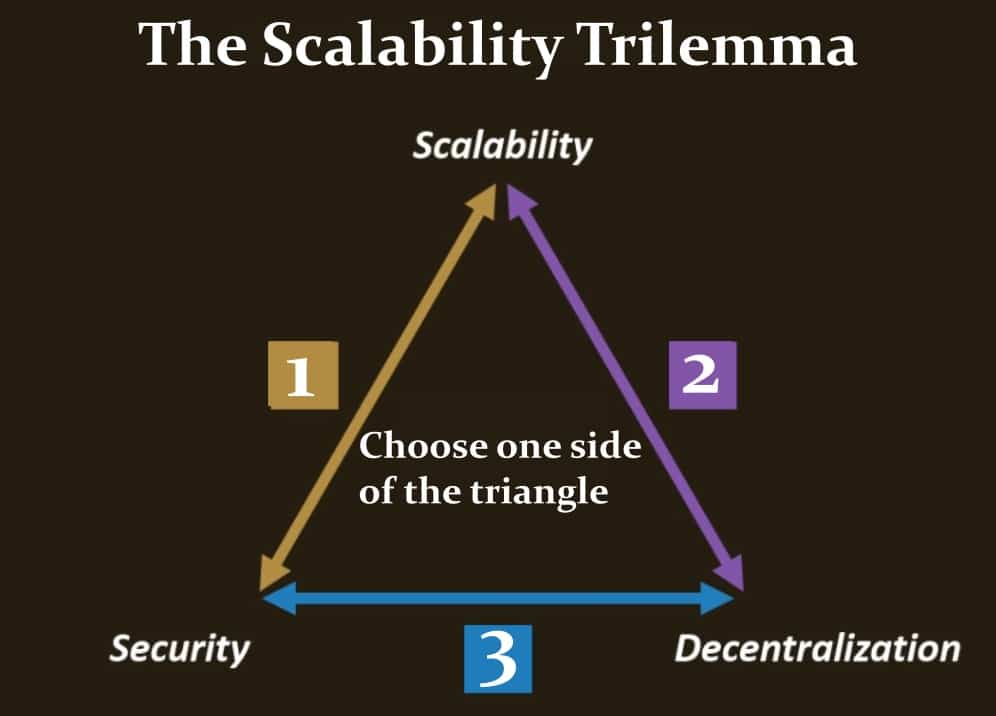
The Blockchain/Scalability Trilemma has Proven to be a Problem for Blockchain.
This scalability trilemma has proven to be incredibly difficult to overcome, one project that has an interesting approach to this problem is Algorand, and you can learn more about how they overcame the trilemma in our in-depth Algorand review.
It wasn't long before the popularity of the Ethereum blockchain was established and network congestion became a real issue. With more users clamouring for block space, the current throughput of 7-15 transactions per second was not able to meet the demands. For reference, Visa and Mastercard handle thousands of transactions per second. At this time, ideas on how to improve the scalability of Ethereum emerged which led to a number of scaling solutions.
Broadly speaking, there are two types of scaling solutions, known as on-chain and off-chain solutions. The on-chain solution requires changes to be made to the Ethereum network. This is going to be in the form of sharding, which is the next phase in the Ethereum upgrade coming up in the near future. Off-chain solutions are changes that occur indirectly on the network to increase transaction speed and throughput (more transactions per second).
As these solutions take place in a separate layer from the mainnet, they are commonly referred to as Layer-2 scaling solutions. This layer provides users the option of handling transactions on their own before handing over the final batch to be written on the Ethereum mainnet. There are 4 types commonly used:
Roll-ups
Transactions are bundled together, or “rolled up” like a carpet on the layer-2. These transactions are submitted in batches to the Ethereum mainnet for final confirmation. There are two types of roll-ups favored by different parties. Optimism and Arbitrum One both use Optimistic roll-up in their operations. This type of roll-up assumes that all the transactions are true and honest unless proven otherwise within 7 days, making it fraud-proof.
The second type of roll-up is zero-knowledge (zk) roll-up. This type generates a cryptographic proof, also known as “validity proof” that acts as a proxy for the batch of transactions it represents. It's like someone proving they are of legal drinking age without having to show their ID. Loopring and zkSync are two of the blockchains that uses this type of roll-up.
State Channels
This type of off-chain scaling solution allows two parties to transact on their own for multiple transactions, with the first and last transaction recorded on the Ethereum mainnet. There are some similarities between this and Bitcoin's Lightning Network. Raiden network uses this as their off-chain solution.
Sidechain
As the name suggests, a side chain is a blockchain that operates next to the main chain. They use a cross-chain bridge to communicate with each other, whether it's to pass tokens or messages/data between them. Users need to lock up the same number of tokens in the main chain that they want to bring over to the other chain. This ensures the same amount will appear in the other chain. For the reverse action, the tokens in the side chain will be burnt (by sending the tokens to a burnt address) before being able to access the ones on the main chain. The side chain is also designed to be EVM-compatible to support smart contracts.
The Polygon network is a stellar example of a sidechain.
Plasma
What makes Plasma stand out from the above is the concept of “child chain” and root chain, which is the Ethereum mainnet. Plasma chains need to submit a cryptographic proof of the child chain to the root chain for transaction validity. Plasma chains can also connect to the Ethereum mainnet using smart contracts. Another interesting feature about Plasma is that they publish Merkle tree roots to the Ethereum mainnet. If the Plasma chain were to be hacked, users can still withdraw their funds via the main Ethereum chain.
Polygon started out as a Plasma sidechain as we mentioned above, but after their rebranding, they also use roll-ups and sharding in their network, ensuring its relevancy in the current period and the future.
Why is Polygon good for Ethereum?
Ethereum is kind of a large, lumbering beast that's not very agile but it's got a huge surface space where lots of other creatures can thrive on it. In some ways, it reminds me of that huge elephant in the One Piece anime that carries a whole world on its shoulders. If we take this analogy to its fullest extent, then Polygon would be the world that relies on the elephant, known as the Animal Kingdom, home to the Minks.
Polygon provides the agility and nimbleness that Ethereum lacks by implementing a number of scaling solutions to help process the transactions sent to the Ethereum network. Not only does this take the burden off Ethereum, but it also lowers the required gas fees, making it more affordable to the everyday user who wants to delve into the rich world of Ethereum.
The network also offers a platform to launch interoperable blockchains. Developers of these blockchains can preset attributes specific to the blockchains they are developing together with various modules to suit the needs of each blockchain. This is something Ethereum lacks in its design. What Polygon does bring about is more diversity at an affordable rate, enticing more developers to work in an EVM-compatible environment.
Polygon (MATIC) vs. Ethereum Layer 1
Even as Polygon is the sidekick to Ethereum, there are a number of benefits that Polygon brings to the Ethereum network that cannot be ignored. While Ethereum trumps Polygon in TVL, number of dApps, and market cap, Polygon holds its own with higher transactions per second and lower gas fees.
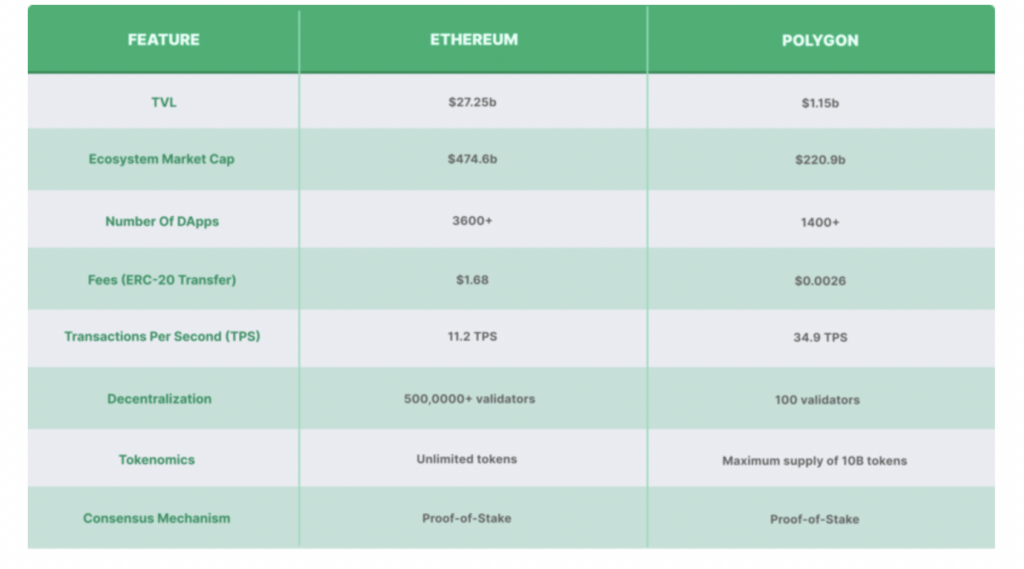
A comparison between Polygon and Ethereum. Image via Coingecko.com
Benefits of Polygon over Ethereum Layer 1
Whether it's minting an NFT or using a DeFi app to get a good deal, you would do better to perform those actions on Polygon rather than Ethereum. Even though gas fees in Ethereum have gone down since The Merge, they are nowhere as competitive as Polygon's fees.

How Polygon compares with Ethereum in fees for dApps. Image via Coingecko.com
Ethereum has an unlimited supply of its native ETH token. Thanks to the burning mechanism put in place, it has the potential to be deflationary. Polygon has a fixed supply of 10 billion MATIC tokens, with more than 90% of it in circulation. As demand for the token rises, it is conceivable that the price of MATIC could prove to be a good investment for investors.
Does the Ethereum 2.0 Upgrade Make Polygon Obsolete?
The short answer is, not likely. Ethereum's roadmap shows that the focus of the blockchain is on improving its own infrastructure and maintaining the operability of the network. This includes finding a way to store historical data so that it doesn't impede on the ability for new data to be written, much like how we back-up old files we don't use to external hard drives, leaving the machine with enough space to store new files.
Polygon is Ethereum's interoperability layer. It provides the infrastructure and capability for individual blockchains to talk to each other, like individual units in a shared apartment block. In this analogy, Polygon is the management office, making sure that all the tenants are happy and thriving in the singular apartment building called Ethereum. It is unlikely that Ethereum would want to take over the duties of the management office as it has enough work to keep it busy in developing the infrastructure of the place.
It is also good to note that Polygon also has its own thriving ecosystem, so regardless of what happens with Ethereum's improvements, most industry thought leaders are in agreement that Polygon isn't likely going to become obsolete once Ethereum is fully upgraded.
Polygon (MATIC) Price and Potential
MATIC, Polygon's native cryptocurrency, has made it to the top 10 on CoinGecko with a $10.4 billion market cap. Around 92% of the maximum supply of 10 billion tokens is in circulation. Its initial trading price of $0.00314376 has been exceeded many times over, reaching an all-time high of $2.92 briefly before settling down in the $1 region. New tokens are minted by staking them in a smart contract as validators are randomly selected to validate new transactions.
Given the number of high-profile partnerships they have signed up, the price potential for the token is on the positive end as there is huge growth ahead. Investors like Greyscale have placed their bets on MATIC as they added it to their Digital Large Cap fund back in October 2022. On the other hand, there are a few clouds on the horizon as some may question the impact Ethereum has on the project with its sharding phase coming up next.
Polygon has had a good start, recently adding more features and signing up more partnerships to lend support to the project. If all goes well, it can see steady growth not only in user adoption but also in its price.
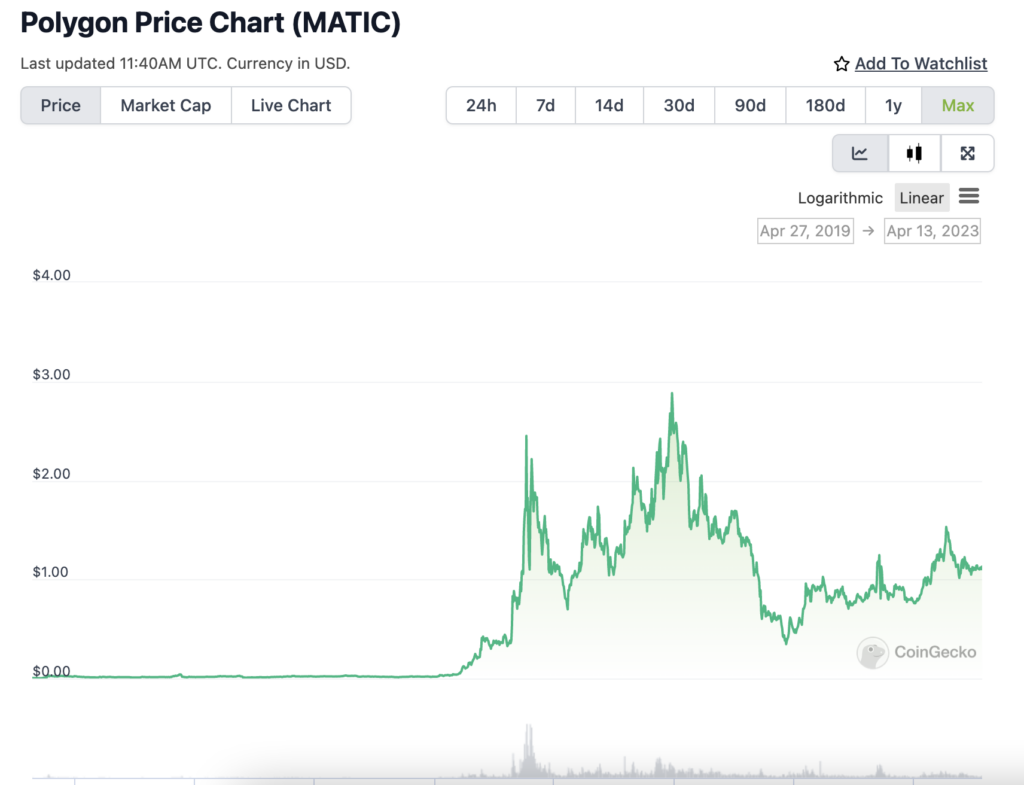
MATIC is not a particularly volatile coin by crypto standards. Image via CoinGecko
How to Buy MATIC Cryptocurrency
There are plenty of choices for obtaining MATIC, with major exchange support from the likes of Binance, OKX, Kraken, Crypto.com etc. Guy has a few centralised exchanges to recommend if you want to buy it with cash. There are also decentralised exchanges but you will need some form of cryptocurrency to exchange for it. The most common types used are stablecoins. There are also crypto shops that sell you the MATIC token but you will need to provide a wallet address to them to send the tokens.
Where to store MATIC Tokens
Most of the wallets in the market can store your MATIC tokens safely. For ease of use, hot wallets such as Metamask are a popular option. If you plan to hold on to them for a while, then cold wallets are your best bet. Ledger, Trezor, and Ellipal are solid cold wallet choices for the storage of MATIC.
Top Projects on Polygon
Being the multipurpose chain that it is, Polygon, long known for being home to some of the top DeFi dApps, is also now known as the no. 2 gaming platform for Web3 games. The rise in gaming ranks is attributed to the formation of Polygon Studios in July 2021. In this section, we briefly look at some of the top dApps on the network, just to give you an idea of the network's capabilities.
- AAVE – the top DeFi protocol with the highest amount of TVL at $342.72m, according to DeFi Llama, can be found on Polygon.
- Aavegotchi – this project was launched by AAVE, and features NFTs of ghosts, similar to the AAVE ghost icon. These ghosts live in the Gotchiverse, and can be procured in two ways: summoning an Aavegotchi or picking one up at the Aavegotchi bazaar.
- Uniswap V3 – the top decentralised exchange in the crypto space is available on Polygon by popular consensus since December 2021. Trading volume for the exchange on the Polygon network is around $38 million, according to CoinMarketCap, compared to the $99.88 million for the exchange across all the networks.
- OpenSea – the top NFT marketplace has a presence on the Polygon network. Cheap gas fees and fast transaction speed are a definite plus for NFT traders.
- Decentraland – the project that popularised the term “Metaverse” has a footprint on Polygon too.
Polygon (MATIC) Review: Closing Thoughts
The Polygon network is a thriving ecosystem with plenty of activity happening on it. Even though total value locked (TVL) on Polygon is only $1.1 billion, which is a fraction compared to $30.69 billion on Ethereum, it has a very strong and vocal community that has supported the expansion of the project from its early days as a sidechain scaling solution to the multi-faceted network it has become.
The success of Polygon Studios and the spate of high-profile partnerships with Reddit, Meta, and DraftKings speaks to big plans ahead for the project. It also doesn't hurt to be selected as the blockchain of choice for Disney’s Accelerator program, and our very own Top Defensive Crypto Investments list. When it comes to the NFT market, Polygon offers traders the chance to trade on the top NFT markets such as OpenSea and Rarible.
The coming period after the Ethereum upgrades are completed will be an interesting time for the blockchain network. How quickly it manages to garner developers to build on its own chain as a doorway into Ethereum will be key to its growth. At the same time, once sharding on Ethereum is completed, the sidechain will also need to find ways to stay relevant as it faces fierce competition amongst other Layer-2 scaling solutions.
Polygon Matic FAQs
What is Polygon (Matic)?
The Polygon network, formerly known as Matic, is a sidechain that helps the Ethereum network handle transaction processing using Plasma. It is also a blockchain project that provides development tools such as the Polygon SDK to make it easier for developers to build dApps that are compatible with the Ethereum blockchain.
What does Polygon (Matic) actually do?
There are two parts to the blockchain project. One part is as a sidechain that helps Ethereum process transactions at much higher speeds and a fraction of its costs. The other part is as a platform that brings together other EVM-compatible blockchain networks with cross-chain messaging and developer tools that enable a one-click solution for developers to launch their projects on Ethereum.
Is Polygon (Matic) as good as Ethereum?
Ethereum is the foundation that Polygon relies heavily on. It's fair to say that without Ethereum, Polygon would not have far to go as its role is to be a strong supporting player for the Ethereum network. That being said, Polygon has certain attributes that Ethereum lacks. These attributes complement the Ethereum network, making it more agile.
Does Polygon (Matic) have a future?
The future of the Polygon network is looking very bright with a number of high-profile partnerships and the success of Polygon Studios, the gaming arm of the network. These partnerships straddle both sides of the fence as regular businesses such as Starbucks and Nike join Web3 dApps like Uniswap and AAVE to offer their services to users.